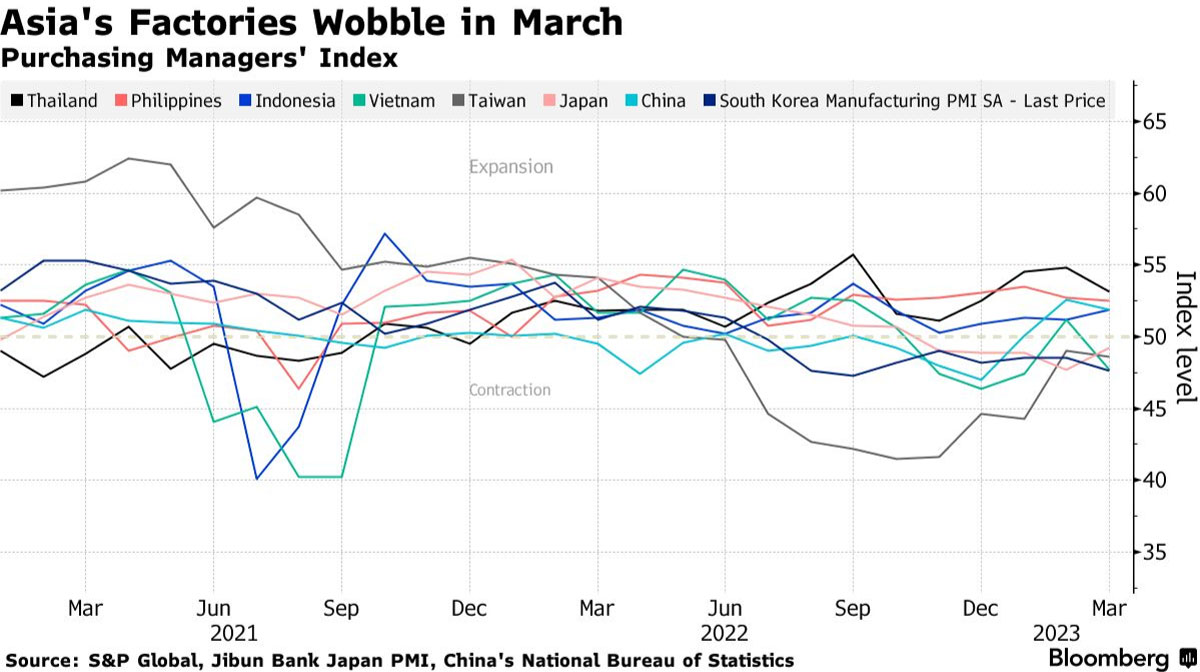
Surveys of purchasing managers at factories across Asia indicated a continued divergence between North and South in March.
Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, all experienced contraction in their manufacturing sectors. North Asian economies are grappling with subdued demand, elevated inflation, and borrowing costs, as well as geopolitical risk and volatility in the semiconductors industry. The global economic outlook is plagued by rising risks of recession, posing challenges for these export powerhouses.
Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan in Contraction Territory
Japan’s manufacturing sector registered a 49.2 reading, up from 47.7 last month, according to the au Jibun Bank and IHS Markit PMI. South Korea slipped to 47.6 from 48.5, marking its worst performance since September. Taiwan’s factory gauge remained in contraction territory, sliding to 48.6 from 49 the previous month.
Southeast Asia’s Manufacturing Outlook in Expansion
In contrast to their North Asian counterparts, Southeast Asian countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and the Philippines saw expansion in their manufacturing sectors. Indonesia’s PMI ticked up to 51.9 from 51.2, marking its best showing since September. Thailand and the Philippines eased slightly but remained in expansion, while Vietnam slipped to 47.7 from 51.2, and Malaysia posted a slight contraction at 48.8.
Southeast Asia’s Economic Recovery Boosted by Technology
“Optimism across the region remained strongly upbeat, and with inflationary and supply chain pressures subsiding, this bodes well for the recovery of the sector,” said Maryam Baluch, economist at S&P Global Market Intelligence, referring to the Southeast Asia region. Technological advancements in these countries are expected to play a vital role in driving economic recovery and improving the manufacturing outlook.
China’s Manufacturing Expansion Continues
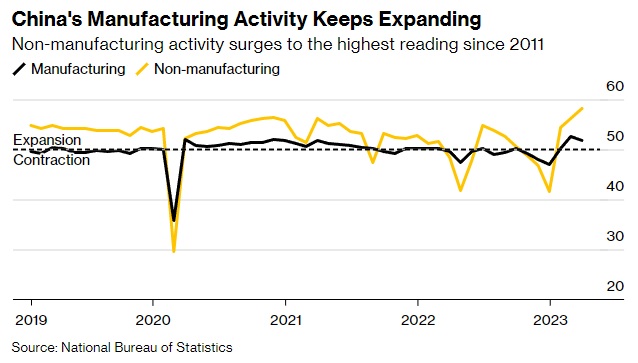
China’s manufacturing sector continued to expand in March, albeit at a slower pace, with the official PMI easing to 51.9 from 52.6 the previous month. The National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) attributed the expansion to local government measures promoting consumption and households’ willingness to spend and travel. Furthermore, warmer weather helped kickstart construction projects across the country.
China’s Economic Rebound Led by Services Activity
The NBS indicated that services activity would likely continue to lead China’s economic rebound, as various PMI figures were released on Friday. The increasing adoption of emerging technologies in the services sector is expected to contribute to the nation’s ongoing economic recovery and maintain its manufacturing expansion.
If you are able, we kindly ask for your support of Logll Tech News today. We appreciate it.

Sergio Richi
Editor, Logll Tech News
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ New Releases
jumper Laptop 16 Inch FHD IPS Display (16:10), Intel Celeron Quad Core J4105, 4GB DDR4 128GB Storage, Intel UHD Graphics, Windows 11 Laptops Computer with Four Stereo Speakers, Type-C, Numeric Keypad.
$279.98
MELIUNA Laptop 16 Inch FHD IPS Display, 128GB ROM 4GB DDR4 Windows 11 Laptops with Intel J4105 Quad Core Processor, Intel UHD Graphics 600, 5G+2.4Ghz WiFi, 2*USB 3.0, Type-C, 1TB SSD Expansion Slot
$279.99
Apple 2023 MacBook Pro Laptop M2 Pro chip with 10‑core CPU and 16‑core GPU: 14.2-inch Liquid Retina XDR Display, 16GB Unified Memory, 512GB SSD Storage. Works with iPhone/iPad; Space Gray
$1,780.66
Best Offer Today
Conclusion: Technology as a Catalyst for Economic Recovery in Asia
In conclusion, the latest advancements in technology are playing a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of Asia amidst the ongoing North-South manufacturing split. While North Asian economies face challenges in their manufacturing sectors, Southeast Asian countries and China continue to experience growth, driven in part by emerging technologies. As the global economic outlook remains uncertain, embracing technological innovation will be essential for bolstering economic recovery and enhancing the competitiveness of the region’s manufacturing industries. Governments and businesses in Asia must continue to invest in and adopt new technologies to ensure a sustainable and robust economic future for the continent.











